Easy Voice Control: Getting Started with the DFRobot Gravity Offline Speech Recognition Module
Introduction
Voice control is becoming increasingly common in smart homes, human–machine interaction, and creative maker projects. However, many speech recognition solutions rely on cloud services, which can raise data privacy concerns and make them unusable without an internet connection. The DFRobot Gravity Offline Speech Recognition Module (SEN0539) addresses these challenges head-on. It delivers accurate speech recognition entirely offline, enabling robust voice interaction without any network dependency.
This article introduces the key features, advantages, and integration process of the DFRobot Gravity Offline Speech Recognition Module (SEN0539). Using a practical example on an Arduino development board, the project demonstrates how to quickly implement offline voice control and unlock the potential of local speech interaction.
Core Features and Advantages of the Gravity Offline Speech Recognition Module (SEN0539)
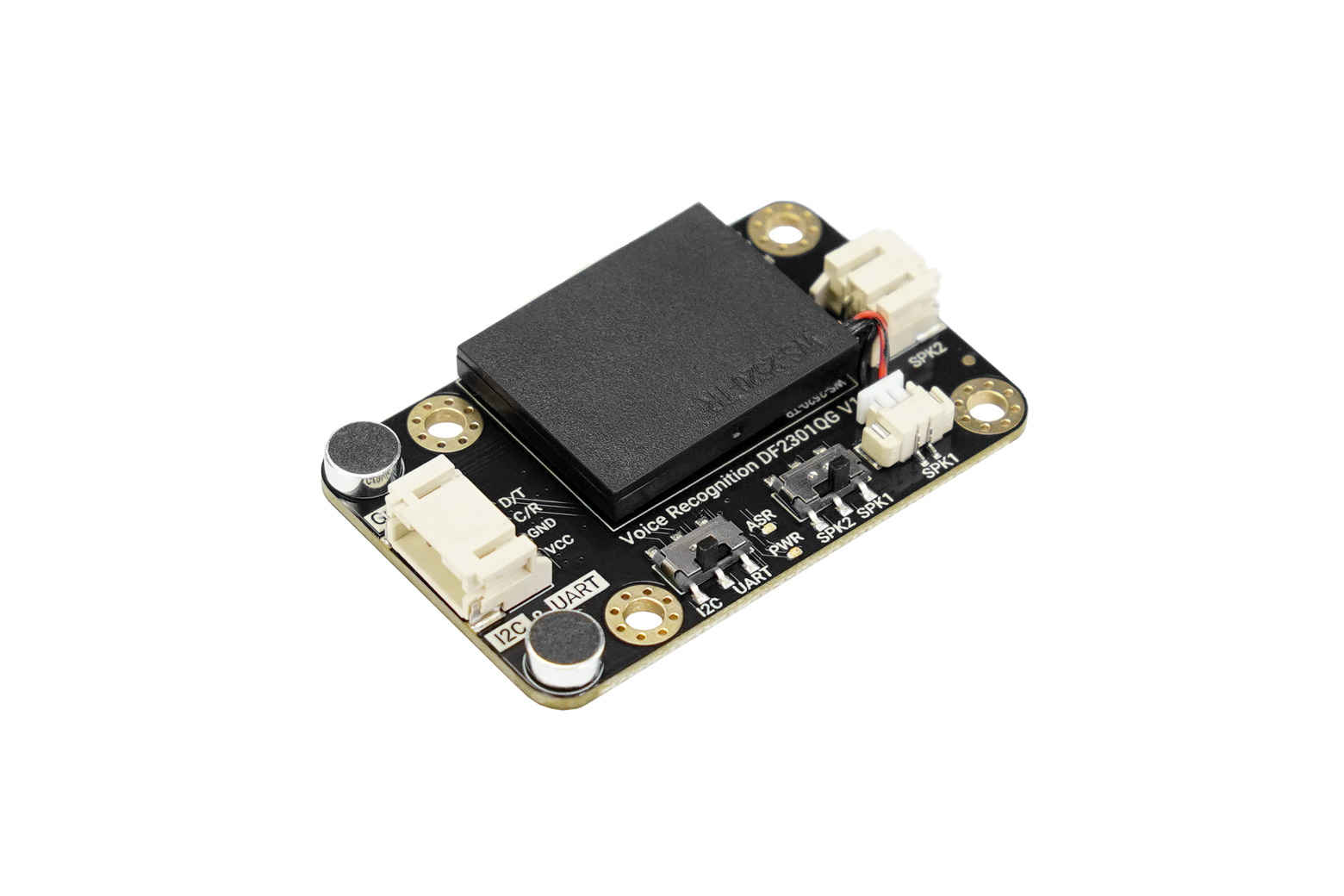
With its thoughtful design and powerful functionality, the DFRobot Gravity Offline Speech Recognition Module stands out in the offline voice recognition space. Its main strengths include:
1. Fully Offline Operation with Privacy Protection
Unlike cloud-based voice assistants, this module integrates an onboard offline speech recognition chip and operates independently without internet access. Voice data never leaves the device, ensuring strong privacy protection. This also makes the module ideal for outdoor projects, educational environments, and scenarios with unstable or unavailable network connectivity.
2. Rich Built-in Commands and Customization
The module comes preloaded with 121 commonly used voice commands covering areas such as education and smart home control, including phrases like “play music,” “open the door,” and “turn on the light.” These commands work out of the box with no configuration required. In addition, it supports up to 17 user-defined commands. Through a simple learning mode, users can record commands in any language or even non-verbal sounds, greatly enhancing flexibility and creativity. For example, voice commands can be used to control a fan or switch modes on a HuskyLens AI vision module, such as face recognition, object recognition, and color recognition.
3. Easy to Use with Broad Platform Compatibility
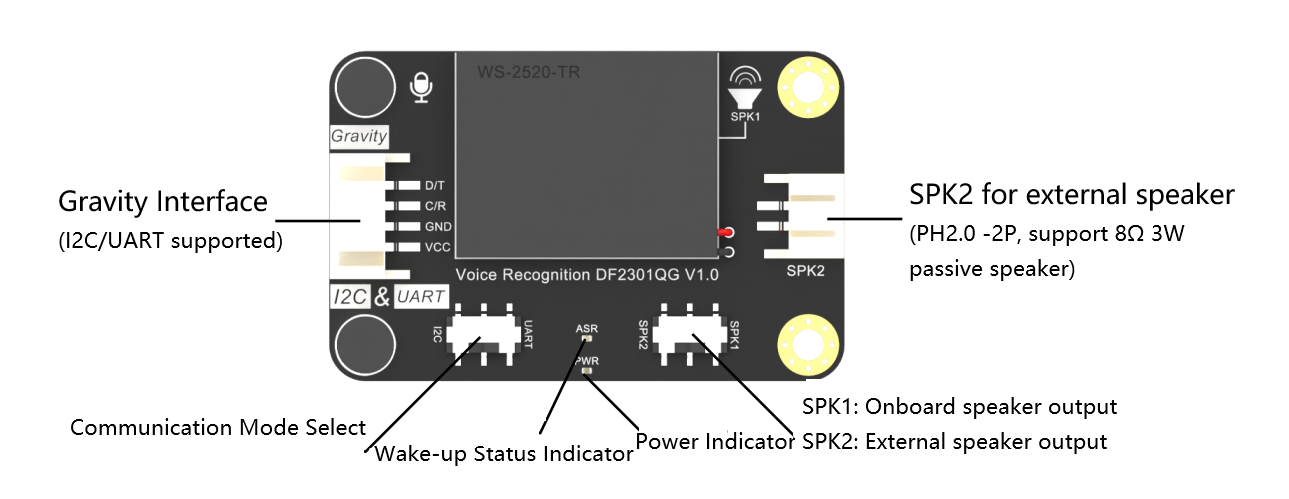
Designed for simplicity, the module is compatible with popular platforms such as Arduino UNO, micro:bit, and ESP32. DFRobot provides comprehensive tutorials for both Arduino IDE and MakeCode. With support for I2C and UART communication, the module integrates seamlessly into existing projects and supports true plug-and-play usage.
4. High Integration, Space Saving
The module features an onboard microphone and speaker, eliminating the need for external audio components. This high level of integration saves space, reduces wiring complexity, and improves overall project stability and cleanliness.
5. Real-Time Voice Feedback
Real-time feedback of recognition results enhances usability and provides a more intuitive user experience.
6. Ongoing Iteration and Optimization
DFRobot continues to refine the module. Version 1.1 (released on May 8, 2025) introduced improvements in physical connectivity and installation, such as a more convenient onboard speaker connector and additional mounting holes. These enhancements make assembly, modification, and deployment easier and more user-friendly.
Application Scenarios and Example Project
Thanks to its versatility, the Gravity Offline Speech Recognition Module excels in a wide range of applications. One representative example is its use in a smart home scenario.
Arduino UNO Voice-Controlled Fan
In this project, the module is used to control a fan connected to an Arduino UNO. By issuing voice commands, users can easily turn the fan on or off. Imagine a hot summer day where simply saying “turn on the fan” instantly brings cooling comfort—no manual switches required. This setup highlights how voice control can significantly improve convenience in everyday life.

Getting Started in Three Simple Steps
One of the biggest advantages of the Gravity Offline Speech Recognition Module (SEN0539) is how quickly it can be put into use. Voice control can be added to a project in just three steps:
Step 1: Connect the Module
The module supports both I²C and UART interfaces, allowing flexible connections to various microcontrollers. To connect it to an Arduino UNO, simply wire the VCC, GND, SDA (or TX), and SCL (or RX) pins to the corresponding power and communication pins on the board. DFRobot’s Gravity connector system simplifies wiring and avoids complicated breadboard setups. Connections for micro:bit and ESP32 follow a similar approach.
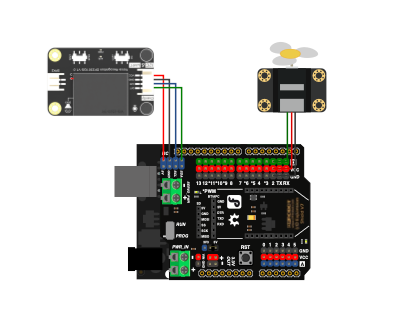

Step 2: Write the Code
DFRobot provides detailed documentation and example code for Arduino IDE and MakeCode, significantly lowering the learning curve. By calling straightforward library functions, developers can initialize the module and read recognized command IDs. Custom commands can be recorded directly using the module’s learning feature, without modifying the program code.


Step 3: Run the Program
After uploading the code to the development board, the voice control system is ready to run. Once the wake word (for example, “Hello, Robot.”) is spoken, the module enters listening mode. When a valid command is recognized, it triggers the corresponding action—such as controlling an LED, switching a fan, or changing HuskyLens operating modes. All of this happens offline, with fast response times and a smooth user experience.

Conclusion
The DFRobot Gravity Offline Speech Recognition Module (SEN0539) is a powerful yet accessible solution for implementing offline voice control. With no internet requirement, support for custom commands, multi-platform compatibility, and a highly integrated design, it is an excellent choice for smart hardware projects, human–machine interaction, and educational applications. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, this module makes it easy to add voice interaction to your projects and take the first step toward a smarter, more intuitive future.










